Understanding Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
Women with PCOS are at increased risk for type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease if not managed properly.
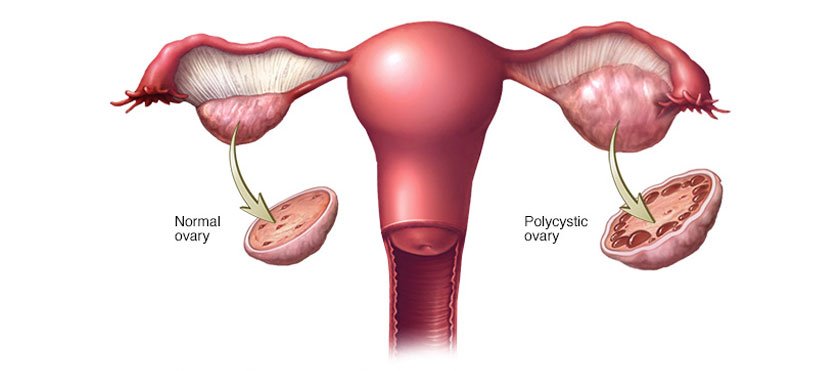
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder affecting women of reproductive age. It can cause irregular periods, hormonal imbalances, and small cysts on the ovaries. PCOS is also a leading cause of infertility and can cause issues with metabolism, skin, and body hair.
What is PCOS?
PCOS is a condition marked by hormone imbalances. The ovaries may not release eggs on a regular schedule, and small fluid-filled sacs (cysts) can form. These changes are often linked to higher levels of insulin and male hormones (androgens). PCOS can impact fertility, periods, and general health.
How Common Is It?
PCOS affects about 1 in 10 women globally. It usually begins in the teenage years and may be undiagnosed until later, often when there are issues with periods or conception
The Silent Epidemic
Despite its high prevalence, PCOS often goes undetected. Studies suggest that up to 70% of women with PCOS may not even know they have it.
PCOS isn’t a rare diagnosis
it’s a health challenge that touches the lives of millions of women across the globe.
Widespread Women's Health Condition
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common hormonal disorders in women of reproductive age.
PCOS is a leading cause of infertility but is highly manageable. Not all women with PCOS have visible cysts. Many women may not know they have PCOS until they try to conceive. PCOS can increase the risk of diabetes and heart disease if not managed. Image suggestion: Fun fact icons or trivia cards for each point.
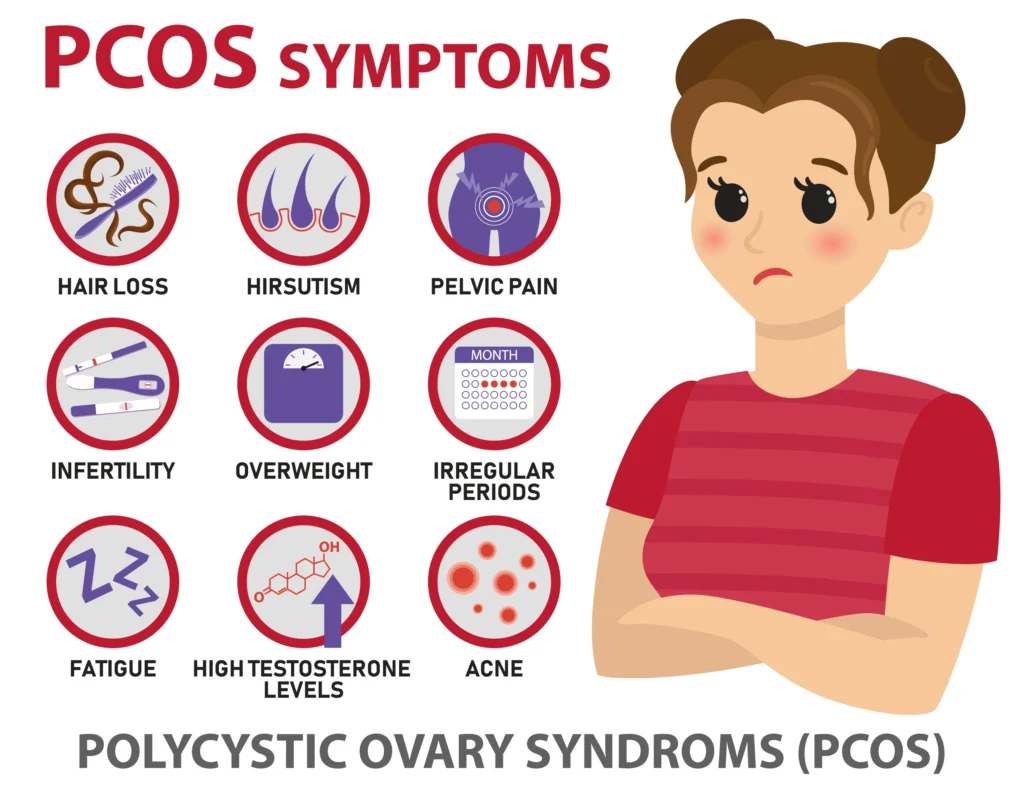
What Are the Common Signs and Symptoms?
What are the common symptoms of PCOS?
Irregular or missed periods
Acne or oily skin
Excess facial/body hair (hirsutism)
Thinning scalp hair
Difficulty losing weight/easy weight gain
Dark, thick skin patches (neck, armpits, groin)
Difficulty getting pregnant
How Is It Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of PCOS involves:
A thorough medical history and symptom review
Blood tests to check hormone levels (like androgens, insulin)
Ultrasound to look for cysts on the ovaries
Note: Not all women with PCOS have ovarian cysts, and not all ovarian cysts signify PCOS. The diagnosis is based on a combination of symptoms and test results.
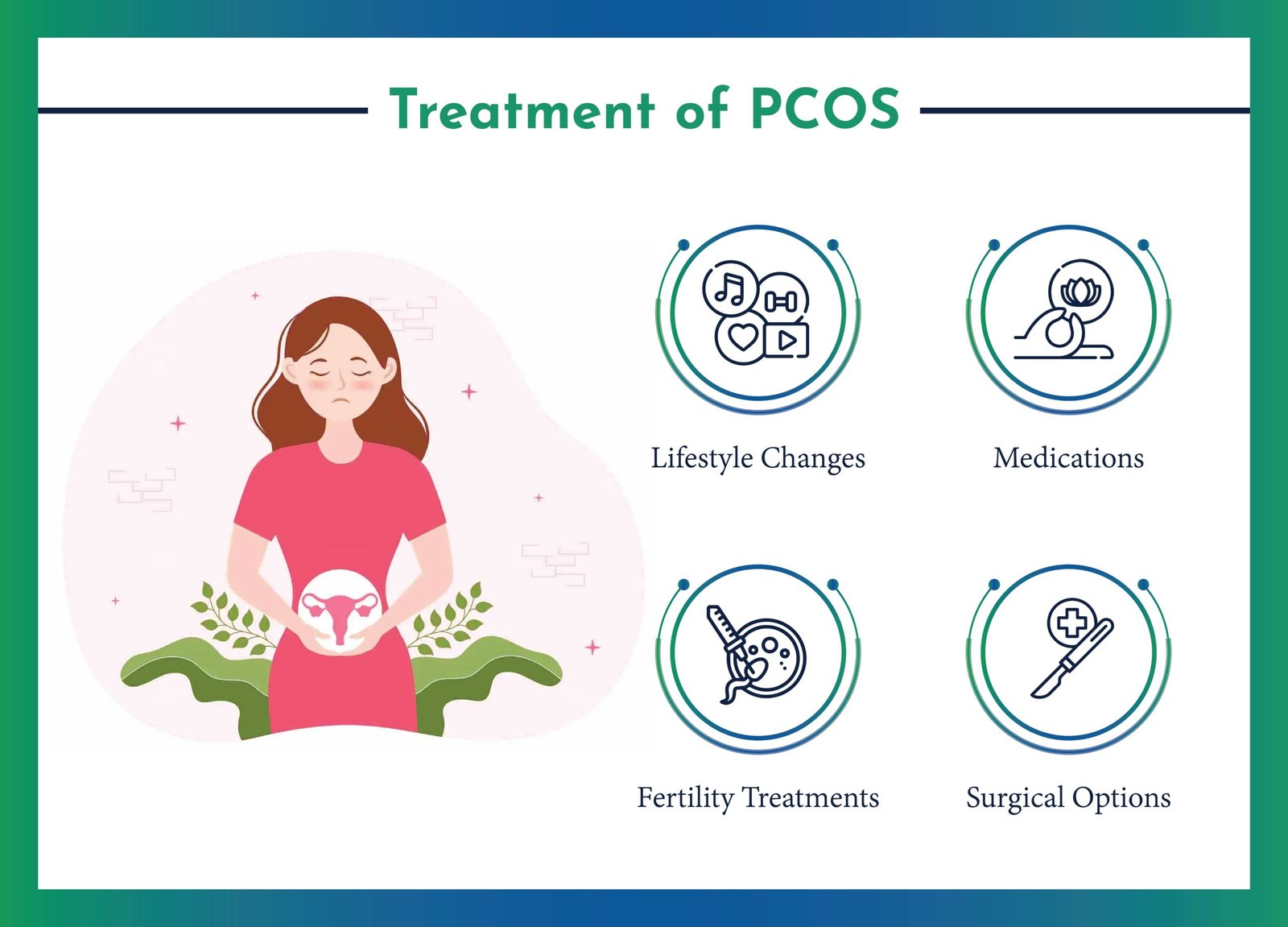
What Are the Treatment Options?
PCOS treatment focuses on symptom management. Options include:
Lifestyle changes: Healthy eating, exercise and weight management (often first line)
Hormone regulation: Birth control pills or hormonal IUDs for period regulation and to reduce acne/excess hair
Fertility support: Clomiphene or Letrozole for those trying to conceive
Insulin sensitizers: Metformin may improve insulin resistance, weight, and ovulation
Regular follow-up with your gynecologist is essential to manage long-term risks like diabetes or heart disease.
Endometriosis Treatment in Abu Dhabi
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical advice if you:
Have irregular or missed periods
Notice unwanted hair growth or acne
Are struggling to get pregnant
Early diagnosis and support improve outcomes and long-term health.
Conclusion / Call to Action
PCOS is common but treatable. With the right care plan, most women can manage symptoms, improve fertility, and reduce long-term health risks. Don’t hesitate to make an appointment if you have symptoms or concerns.